What is the main difference between primary and secondary succession? What does secondary succession stand for? What happens during secondary succession?
Which of the following is an example of secondary succession? The stages of secondary succession are similar to those of primary succession: insects and weedy plants (frequently from surrounding ecosystems) are often the first to recolonize the disturbed area , and these species are replaced by hardier plants and animals as time goes on. If this landscape remains undisturbed for a long enough time, the evolving biological community can once again attain a stable ecological structure. Primary succession Primary succession begins in barren areas, such as on bare rock exposed by a retreating glacier. Location of occurrence.
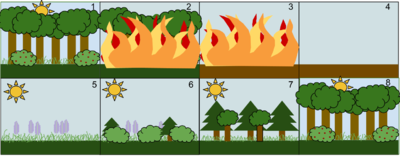
Unlike primary succession, secondary succession begins in an environment with pre-existing soil. On a rock where the vegetation has been destroyed by fire, the secondary succession starts with lichens again. The rich, organic matter left over by the fire helps in a quick succession and soon rich conifers are seen in the area.
It begins with the appearance of pioneer species – lichen, mosses and fungi – that can grow on rocks and exposed land. These are small, simple organisms that can survive harsh conditions, fix inorganic carbon and nitrogen, and accelerate the process of weather. See full list on biologydictionary. These include:While some of these are natural events, some are anthropogenic, or manmade.
Though it appears as if the region is ‘dead’, the soil remains fertile and contains enough organic matter to support the reappearance of life. Grasses are among the first species to appear, quickly followed by shrubs and small trees. The major difference between primary and secondary succession is the quality of the soil.
Abiotic Factors – The non-living, physical and chemical components of an ecosystem. Climax Species – Plants seen in stable and mature ecosystems that have reached a steady state. Example: white spruce trees. Pioneer Species – Species that first appear in an uninhabited area.
Choose all that apply. An Expert Will Answer in Minutes! The pioneer species of secondary succession are the species already present within the previous ecosystem.
Soil is present in the area where secondary succession begins. Humus is present before the very beginning. In contrast, secondary succession is the re-colonization of a region after a significant disturbance.
The end result of succession is the establishment of a climax community. Pioneer species for secondary succession are adapted differently- they grow quickly, can disperse quickly and have a short life span. When secondary succession occurs, communities are usually reintroduced to the ecosystem more quickly than happens during primary succession.
Plant and animal communities already existed before the disturbance that leads to secondary succession. Therefore, the soil is often richer than in areas where primary succession occurs. This video describes the process of ecological succession and compares primary to secondary succession. Teachers: You can purchase this PowerPoint from my on.
The idea of a climax community. The difference between primary succession and secondary succession is _____. Succession as progressive change in an ecological community.
Secondary succession occurs in an area which has been denuded recently. Primary and Secondary are two types of ecological succession. When natural communities are developed in barren habitat with no soil or extremely less soil, it is called primary succession.
Abiotic factors such as water, win and species like algae and lichen have a significant role to play in primary succession. Primary colonizers are involved in primary succession , whereas no need of primary colonizers in secondary succession. Soil is already present in secondary succession , but in primary succession , primary colonizers involve in creating soil. The disturbance may be an external or an internal factor.

An example of secondary succession is the recolonization of an area damaged by fire. Another difference between primary and secondary successions is the nature of the habitat. In primary succession , living things colonize a barren lan which means it lacks topsoil.
This slide presentation will teach students what is ecological succession , primary and secondary succession , pioneer species as well as help them process the information through a Venn diagram, discussion questions and a procession activity. What is one difference between primary and secondary succession. The orderly natural changes and species replacements that take place in the communities of an ecosystem. The colonization of barren land by communities of organisms.
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.