These electronic components are also widely used in starter circuits for fluorescent lamps. See full list on electronics-notes. As discrete components they may be contained in small leaded packages, they can be obtained in surface mount packages, in large packages that bolt to a chassis, or a variety of other packages.

DIACs come in a variety of formats. The actual breakdown voltage will depend upon the specification for the particular component type. By equalising the switching characteristics of these TRIACs, the level of harmonics generated when switching AC signals can be reduced.
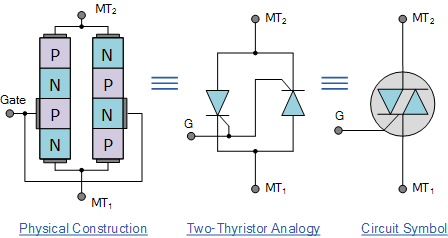
Despite this, for large applications, two thyristors are generally used. Interestingly their behaviour is somewhat similar to that of a neon lamp, although they offer a far more precise switch on voltage and thereby provide a far better degree of switching equalisation. This device helps make the switching more even for both halves of the cycle. When breakdown occurs, the diode enters a region of negative dynamic resistance, leading to a decrease in the voltage drop across the diode an usually, a sharp increase in current through the diode. The basic construction of diac consist of two terminals namely MTand MT2.
A diac is a P-N-P-N structured four-layer, two-terminal semiconductor device, as shown in figure. Construction of a Diac. MT and MT X are the two main terminals of the device. There is no control terminal in this device. From the diagram, a diac unlike a diode, resembles a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) but with the following exceptions.
What is the structure of a diac? The triac is a two-way SCR with one gate terminal. A diac -triac combined package is called as Quadrac. However, it has an important role in Triac triggering and other thryristor based circuits. Several gate triggering circuits use this device for achieving greater triggering stability and noise immunity.
It is a two terminal bidirectional switching device. These terminals are not named as anode and cathode in case of normal diode. This indicates that this device can be used in either direction.
It has two arrows in both directions, which means that it conduct for either polarity of the supply voltage. Transistor is a three terminal device, whereas the diac is a two terminal device. The three regions in diac are equal in size. A three layer structure is more commonly used than other structure.
In PNP form, two terminals are connected to the outer silicon P-regions separated by N region. This structure is same as PNP transistor with no base connection. As soon as the supply voltage whether positive or negative is applied across the terminals of a diac , only a small leakage current flows through the device. So the device operates in either forward or reverse blocking modes.
When the terminal Tis positive with respect to ter. Then, it starts conducting and exhibits negative resistance characteristics, i. The voltage drop during the conduction is very less and is equal to the ON state drop of the diac. The current flow increases quickly when it comes into the conduction mode.
Therefore, for a safe operating level of this conduction current in either direction, a resistance is connected in series with the diac. The region OA in the portion of the characteristics is the blocking region. Under these conditions diac operates as an open switch.
Once the positive or negative applied voltage is more than the respective breakdown voltages that means at point A in the above figure the diac begins to conduct and the voltage drop across the device becomes few volts. The portion AB represents the conduction of diac. This conduction continuous until the devic. Since the triac requires either positive or negative gate pulse to come into the conduction state.
Although it can be triggered by a simple resistance firing circuit, for a reliable and faster turn ON, a diac is used in series with the gate. Hence the diac is mainly used as a trigger device to the triac. In today’s market, there are several Diac-Triac matched pairs are available for different control circuits. By using this, power fed to the lamp is controlled smoothly. The variable gate voltage is produced by RC arrangement at the gate terminal of triac.
As the input voltage is applied to the circuit, cand cstarts charging at a rate determined by the resistance R2. Whenever the voltage across the capacitor cexceeds the breakove. This circuit operation is also similar to the above circuit. The LC combination across the triac reduces the rate of rise of voltage during the turn OFF of the triac. The positive and negative half cycle of the input voltage to the heater is controlled by adjusting the resistance R2.
For all variable positions of R, a smooth control ensued by placing resistance Racross. TRIAC (triode for alternating current) is a generic trademark for a three terminal electronic component that conducts current in either direction when triggered. The thyristor consists of a four layer PNPN structure with the outer layers are referred to as the anode (P-type) and cathode (N-type).
The control terminal of the thyristor is named the gate and it is connected to the P-type layer located next to the cathode. As a result the thyristor has three junctions rather than the one junction of a diode, and two within transistors. They are numbered serially with J1being nearest to the anode.

Although it is possible to use a variety of different materials for thyristors, silicon is the most popular. The trade name for this type of device - silicon controlled rectifier - also indicates that silicon is the most popular material. Silicon provides good thermal conductivity as well as a high voltage and current capability. Another advantage is that the processes for silicon are more mature, and hence cheaper to run, than those for other materials. Nevertheless silicon still remains the most popular substance.
The level of doping varies between the different layers of the thyristor. The cathode is the most heavily doped. The gate and anode are the next heavily doped. The lowest doping level is within the central N type layer.
This is also thicker than the other layers and these two factors enable a large blocking voltage to be supported. Thinner layers would mean that the device would break down at lower voltages. In view of the very high currents and power levels that some thyristors are used to switch, thermal considerations are of paramount importance. The anode of the SCR or silicon controlled rectifier is usually bonded to the package since the gate terminal is near the cathode and needs to be connected separately. This is accomplished in such a way that heat is removed from the silicon to the package.
Apart from the internal considerations, the external heat-sinking considerations for the thyristor must be carefully implemented otherwise the device may overheat and fail. The asymmetric thyristor is characterised by what is termed a cathode short and an anode short. The short between the P and N regions has the effect of adding a resistor between the junctions, i. This has a variety of effects including reducing carrier lifetime and improving the transient response time. Different structures are used by different manufacturers for different applications. Also silicon is by far the most widely used material for thyristors.
Thyristors or SCRs, silicon controlled rectifiers are well established and the technology is very stable. The devices are widely used for power switching, an application to which they are very suited. More Electronic Components: Resistors Capacitors Inductors Quartz crystals Diodes Transistor. Triac Basic Structure Operation and Working of a Triac.
Though the triac can be turned on without any gate current provided the supply voltage becomes equal to the breakover voltage of the triac but the normal way to turn on the triac is by applying a proper gate current. Their internal structure vi ch. The symbol consists of three terminals which are Gate, Anode or Main terminal. The two terminals are labeled as an anode or anode main terminal MTor MT2. When a triggering current is applied to triac gate, it is switched ON by means of its inbuilt diodes embedded back-to-back between G terminal and and Aterminal.

The diac is a two-way breakover triggering device. Therefore, the ratings of the traics considerably lower than the thyristors. The two leads are connected to p-regions of silicon separated by an n-region.
The structure of diac is very much similar to that of a transistor. DIAC and its schematic symbol.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.