Support for Ardern as preferred prime minister was at compared to for Collins. Under New Zealand’s proportional voting system, larger parties typically. What are the different methods of voting?

What is an example of proportional representation? If n of the electorate support a particular political party or set of candidates as their favorite, then roughly n of seats will be won by that party or those candidates. If a party wins percent of the national vote, it wins percent of the. Proponents claim that mixed-member proportional voting (MMP) is the best of both worlds: providing the geographical representation and close constituency ties of single-member plurality voting along with the fairness and diversity of representation that comes with PR voting.
Representation of all parties in a legislature in proportion to their popular vote. It aims to produce election where winners gain seats in proportion to the votes they secure. Whether a state assigns it votes by a winner-take all system or another way can have important consequences because different vote allocation methods can produce different election. See full list on electoralvotemap. Both states have produced one split vote.

The remaining two electoral votes in Maine and three in Nebraska went to the other party’s candidate. Although an improvement over winner-take-all system’s potential incongruity between the popular and electoral college vote, the Nebraska and Maine electoral vote allocations are imperfect solution for a couple of reasons. Senate is not apportioned by population. While many of the other state legislatures have considered laws to change how their states allocate their electoral votes, none have passed. State legislators, not surprisingly, vote for and.
House of Commons (seats). They have proven to be particularly effective at producing representative bodies from areas with broadly diverse or divided populations. The majority of proportional representation voting systems use the party list. A proportion representation system is a multiple winner method and works by.
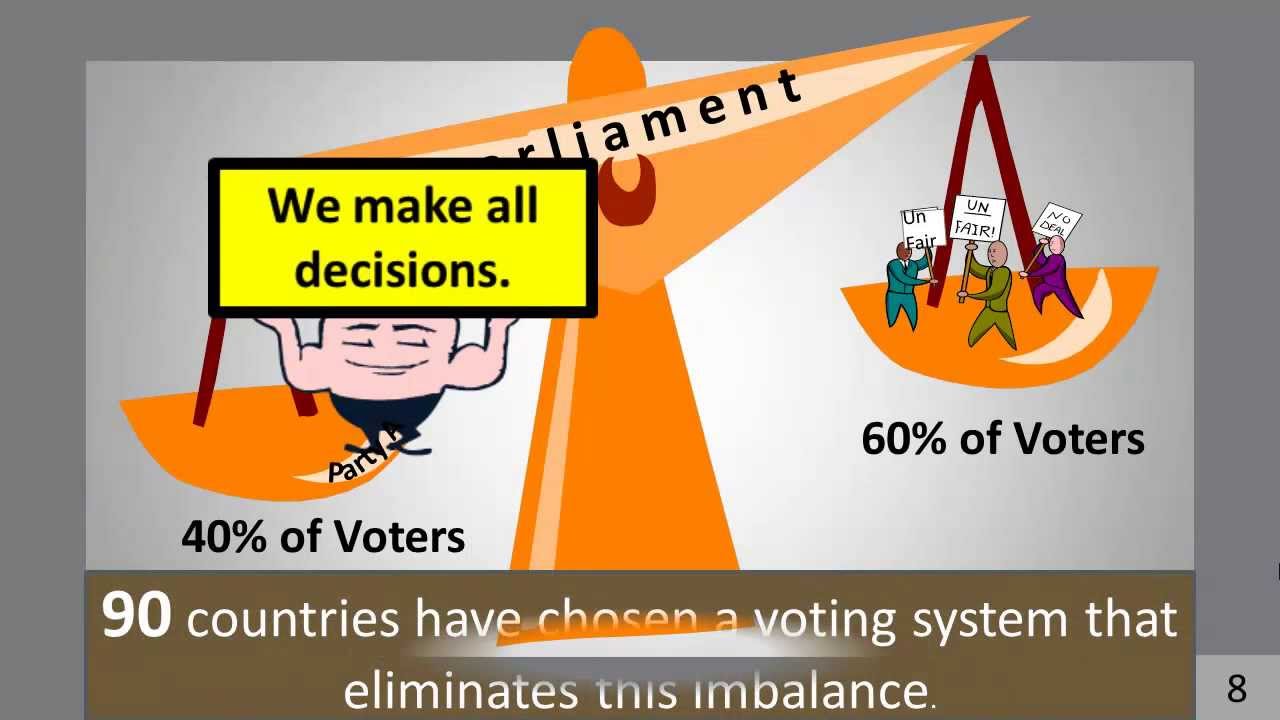
Proportional voting systems have been in use around the world and in local U. Single Transferable Vote (STV). A more proportional way would mean that a party that received one-third of the vote could expect one-third of the seats in parliament. This means the percentage of seats a party has in the legislature should reflect the percentage of people who voted for that party.
Under PR, parties, groups and independent candidates are elected to the Parliament in proportion to the number of votes they receive. This is because every single vote cast in the election will count towards the number of seats a particular party ends up winning in the legislature. In the Party List PR system, votes – and therefore representation – are allocated proportionally across political parties, allowing the parties themselves to appoint candidates once votes are tallied. Under this vote counting metho the will of the electorate is well represented by the final allocation of seats.
Under the whole-number proportional method for awarding electoral votes, states would enact laws dividing their electoral votes in proportion to each candidate’s share of the popular vote in their state. The whole-number proportional method may initially sound attractive. One might ask how it could be any other way. Popular Vote by State (PVS) is the same as PPV, except all a state’s electoral votes are allocated by popular vote.
For example, if a party. Although proportional and semi- proportional voting methods are used in the United States, winner-take-all voting methods remain the norm. Winner-take-all voting methods. In an election, political parties that earn votes win a number of seats in the representative body that are directly proportional to the number of votes they received in the election.
A political party that wins votes in a particular election is able to win a number of seats in the representative body. The number of seats won is directly proportional to the number of votes they got in the election. PR offers alternatives to first past the post and other majoritarian voting systems based on single-member electoral areas, which tend to produce disproportionate outcomes and to have a bias in favour of.
In our current system Obama got all ten votes while Romney got zero. The Constitution provides for proportional representation in the U.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.